In November 2022, the next UN World Climate Conference will take place in Egypt. It will reconfirm what we have known for years: We have to be more sustainable. And we can be more sustainable – from space. Data from satellites in low-earth orbit allow us to conduct comprehensive real-time research on the climate, make informed decisions and take action. Small launch vehicles from Europe make it possible to transport these satellites and thus form the foundation of a sustainable space travel, called Green New Space.

Spaceflight plays an important, if not crucial, role in creating a global climate data model. Satellite constellations for Earth observation can create a huge data model, a digital twin, of the Earth. Researchers can use this data to observe, research, understand, and act. Transporting the satellites needed to do this into space must also be sustainable and ecological. This must be done in two dimensions in particular: The strategic dimension as well as the technical dimension.
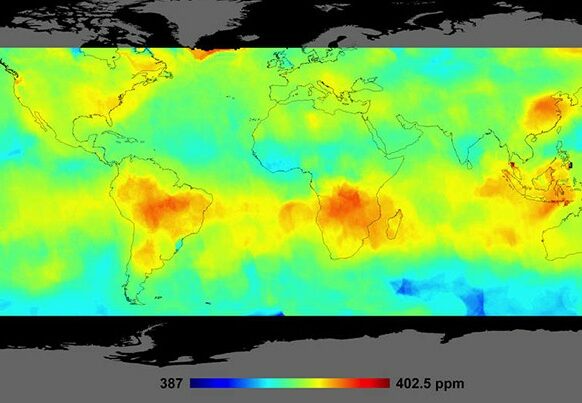
In the case of space travel, it is important to keep reminding ourselves of the enormous benefits it brings: satellites provide data that can not only optimize logistics routes by emission or prevent forest fires, but also actively contribute to climate research and environmental protection. Atmospheric and ecosystem research, e-mobility, determination of fertilizer concentrations, sustainable water management – all these are just a few of the numerous application examples where it is best to work with an overview, from above, from space. In conclusion, rockets, the means to an end, are extremely sustainable on a completely different level: they enable us to better understand and protect our Earth with data from space.
In the long term and from a strategic point of view, one might object that it is getting more and more crowded up there and that space debris has already reached worrying proportions. That’s true. Russia shot down an old Russian satellite in November 2021, causing vast amounts of small, yet highly energetic debris due to its enormous velocity, and thus dangerous to existing and future satellites. Therefore, it is imperative to deal with the prevention and disposal of the same. Orbital stages are being developed that can automatically burn up after some time and even selectively collect space debris beforehand. Services offered by these orbital stages in orbit include refueling, battery replacement or repair work. They work to make satellite constellations decisively more durable and thus more sustainable. Because what can be operated longer does not have to be newly produced and replaced.
Rockets and sustainability are not mutually exclusive. On the contrary: Economy and ecology are not contradictory here, but go hand in hand and have been part of the business idea from the very beginning: climate and environmental protection is one of the main customers of space travel. We are convinced that in the medium term, every industry can and will benefit from data from space. Consciously sustainably designed rockets, with their simultaneously inexpensive, flexible and precise transport into orbit, are a key element of space-based climate and environmental protection. And thus far more than just (very loud) noises and flashy lights. Let´s get into details.

Rockets and sustainability are not mutually exclusive. On the contrary: Economy and ecology are not contradictory here, but go hand in hand and have been part of the business idea from the very beginning: climate and environmental protection is one of the main customers of space travel. We are convinced that in the medium term, every industry can and will benefit from data from space. Consciously sustainably designed rockets, with their simultaneously inexpensive, flexible and precise transport into orbit, are a key element of space-based climate and environmental protection. And thus far more than just (very loud) noises and flashy lights. Let´s get into details.
On the technical side, much has happened in recent years, and a sustainable Green New Space has developed. Reusing stages, for example, not only saves a large part of the total production cost of a rocket, it also saves resources and labor time and reduces the CO2 emissions of production – those who reuse do not have to produce anew. And it works: SpaceX and Blue Origin have been landing and reusing their first stages fully automatically for years.
Tank structures are made of stainless steel. This is available at lower cost, can be processed quickly and with low energy consumption, and also allows corrections to be made: Where composite structures become very expensive and only storable, non-recyclable waste in the event of even the smallest production defects or test damage, stainless steel with its properties is ideally suited for series production. Tank structures made of stainless steel can be simply rolled and welded, and isolated production errors or test losses are of little consequence either ecologically or in terms of time and cost because they can be reused.
At the same time, modern engines with staged combustion are being developed. In these, the exhaust gases from the turbopump are fed into the main combustion chamber. The fuel is burned more completely and thus not only more efficiently but also in a more environmentally friendly way: Thanks to this so-called “closed cycle,” the engine does not eject highly sooty exhaust gases from the turbopump into the atmosphere, as is the case with engines with an open combustion cycle, for example. Additionally, research is being done on other sustainable options like hybrid-rocket propulsion using e.g. wax as a fuel. These are just a few examples of technologies that show that the industry is aware of its responsibilities and is working to incorporate the ecological dimension into its development and business ideas.
On the technical side, much has happened in recent years, and a sustainable Green New Space has developed. Reusing stages, for example, not only saves a large part of the total production cost of a rocket, it also saves resources and labor time and reduces the CO2 emissions of production – those who reuse do not have to produce anew. And it works: SpaceX and Blue Origin have been landing and reusing their first stages fully automatically for years.
Tank structures are made of stainless steel. This is available at lower cost, can be processed quickly and with low energy consumption, and also allows corrections to be made:
Where composite structures become very expensive and only storable, non-recyclable waste in the event of even the smallest production defects or test damage, stainless steel with its properties is ideally suited for series production. Tank structures made of stainless steel can be simply rolled and welded, and isolated production errors or test losses are of little consequence either ecologically or in terms of time and cost because they can be reused.
At the same time, modern engines with staged combustion are being developed. In these, the exhaust gases from the turbopump are fed into the main combustion chamber. The fuel is burned more completely and thus not only more efficiently but also in a more environmentally friendly way: Thanks to this so-called “closed cycle,” the engine does not eject highly sooty exhaust gases from the turbopump into the atmosphere, as is the case with engines with an open combustion cycle, for example. Additionally, research is being done on other sustainable options like hybrid-rocket propulsion using e.g. wax as a fuel. These are just a few examples of technologies that show that the industry is aware of its responsibilities and is working to incorporate the ecological dimension into its development and business ideas.
The coalition agreement of the German Government signed in the end of 2021 in Germany describes space travel and especially the field of NewSpace as a central technology of the future and wants, among other things, to strengthen the national space programme. It demonstrates the importance the coalition and especially the green party, which is part of the coalition, puts on New Space to help achieve a CO2 neutral Germany. Climate protection efforts need solid and continuously updated data as a basis for decision-making, which can only be gathered by satellites.
With its three rocket-building start-ups, Germany has already taken a leading role in European New Space. Building on this, New Space is a crucial piece in the institutional fight against climate change. With its setup of new launchers, Germany has the option to lead in the production of green launch vehicles, which enable the gathering of data that can in turn be used to coordinate climate protection efforts all over the world and allow sustainable services in orbit. What is needed, however, is practical political initiative in the form of institutional launch agreements, economic and structural support for commercial competition and clear regulations. We have everything to lose, so let’s address the problem head-on – based on and with the help of sustainable space travel.
Stay up to date with The Preburner blog and all of our latest posts by signing up.
Copyright 2025 © All rights reserved.
If you’re interested in receiving access to our Payload Users Guide for our Redshift OTV, please enter your details below.
If you’re interested in receiving our press kit, please enter your details below. We’ll review your request and get back to you ASAP.
If you’re interested in receiving access to our Payload Users Guide for our RFA ONE, please enter your details below.
We will get back to you soon.

Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. This category only includes cookies that ensures basic functionalities and security features of the website. These cookies do not store any personal information.
Any cookies that may not be particularly necessary for the website to function and is used specifically to collect user personal data via analytics, ads, other embedded contents are termed as non-necessary cookies. It is mandatory to procure user consent prior to running these cookies on your website.
Analytical cookies are used to understand how visitors interact with the website. These cookies help provide information on metrics the number of visitors, bounce rate, traffic source, etc.
Performance cookies are used to understand and analyze the key performance indexes of the website which helps in delivering a better user experience for the visitors.
Undefined cookies are those that are being analyzed and have not been classified into a category as yet.